What exactly is a muscle?
A muscle is a band or bundle of tissue fibers that have the ability to contract and relax and contribute to movement.
There are 3 types of muscles in the body, skeletal muscle , smooth muscle and caridiac muscle.
We can consciously control Sequeletal muscle, however cardiac (heart) and smooth (mostly within organs) are contracted involuntarily.
Muscles have tendons at their extremities which attach them to bones (usually on 2 different bones). When the muscle contracts this is what creates movements and locomotion within our body.
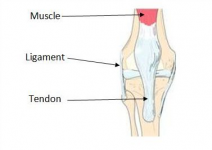 What is a tendon?
What is a tendon?
A tendon is a band of fibrous connective tissue that usually attach muscles to bones. Tendons work with muscles to move bones.
What is a ligament?
Ligaments, like tendons are fibrous connective tissue. Ligaments however connect bone to bone to create joints.
Ligaments can limit certain movements and prevent others. Mainly they play a role in the stability of joints.
Sprain vs Strain ?
A sprain happens to ligaments where as a strain happens to muscles or tendons.
Both happen when the tissue in question is overstretched and/or injured by tearing of the tissue.
A strain happen usually where a muscle and a tendon attach to each other. This musculo-tendinous junction is prone to injury when a person is in action (ex running) and a muscle is involuntarily contracted while being stretched. Symptoms for a muscle strain may include pain , muscle spasms, loss of strength and limited range of motion.
A sprain occurs when a joint is forced outside its normal range of motion and a ligament is injured. Symptoms of a sprain may include pain, inflammation, and possibly the inability to move the affected joint.
S everity of sprains and strains
everity of sprains and strains
Sprains and strains are categorized according to severity. A Grade I (mild) sprain or strain involves some stretching or minor tearing of a ligament or muscle. A Grade II (moderate) sprain or strain is a ligament or muscle that is partially torn but still intact. A Grade III (severe) sprain or strain means that the ligament or muscle is completely torn, resulting in joint instability.
Treatment
As soon as possible, when a injury occurs follow the following P.R.I.C.E
- Protect the area
- Rest the area
- Ice the area for a good 20 minutes 3 times a day
- Compress the injured area to help prevent inflammation ( not too tight though )
-
Elevate the injured area above the height of your heart to prevent inflamation.
Grade I injuries usually heal quickly and combining approprite exercises and stretches can help with regaining original strenght and flexibility.
Grade II injuries are treated the same but might require you to immobilize the joint to allow for proper healing.
Grade III injuries are more severe and more often then not require imobilization and possibly surgery to regain proper function
In all cases its important to be evaluated by a professional so a treatment plan can be created together. With the proper approach most people can heal from sprain and strains without long term side effects.
Daniel Godin, Massage therapist